Hubble Observes a Galactic Distortion
1 min read
Hubble Observes a Galactic Distortion
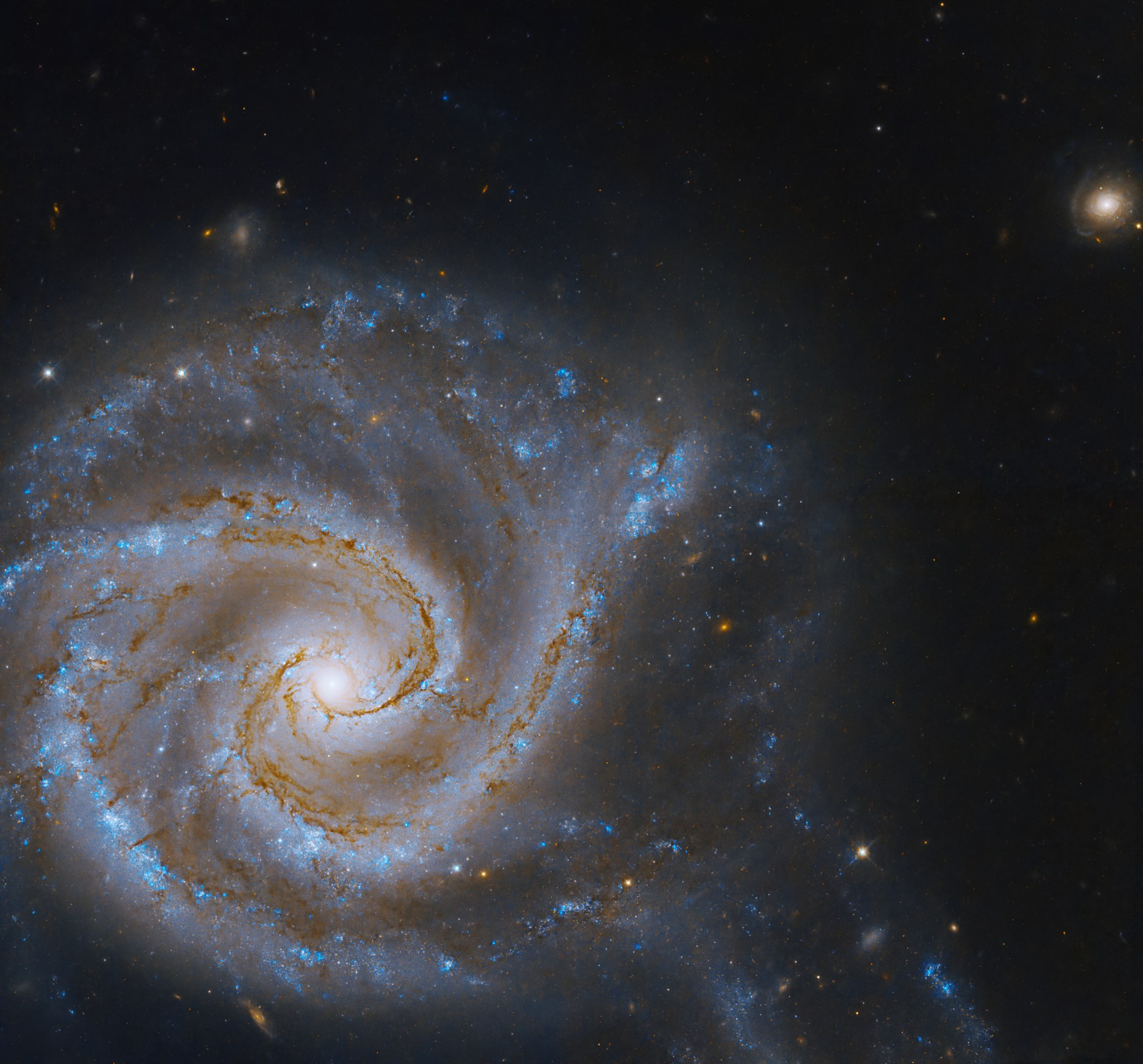

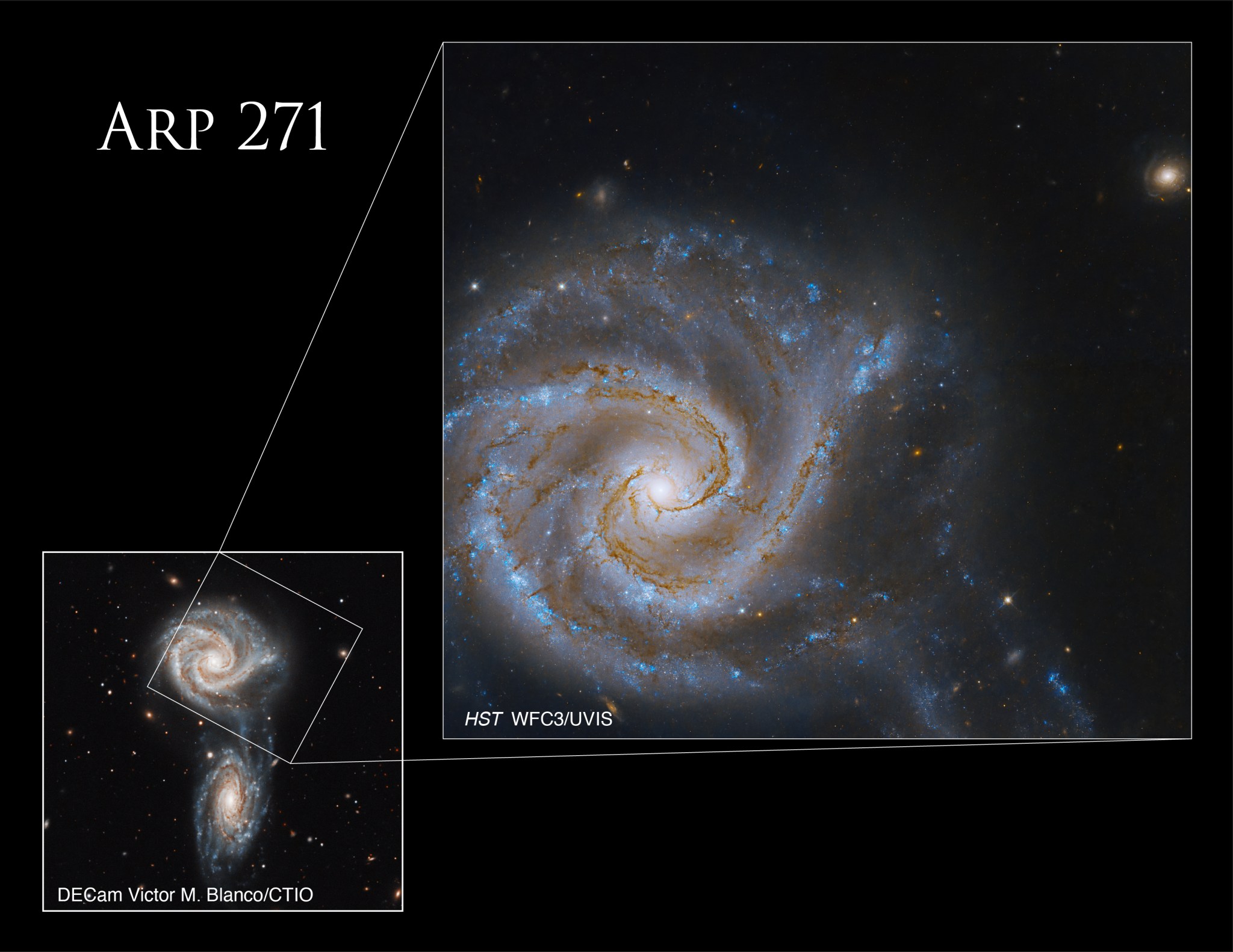
The galaxy NGC 5427 shines in this new NASA Hubble Space Telescope image. It’s part of the galaxy pair Arp 271, and its companion NGC 5426 is located below this galaxy and outside of this image’s frame. However, the effects of the pair’s gravitational attraction is visible in the galactic distortion and cosmic bridge of stars seen in the lower-right region of the image.
In 1785, British astronomer William Herschel discovered the pair, which is locked in an interaction that will last for tens of millions of years. Whether they will ultimately collide and merge is still uncertain, but their mutual gravitational attraction has already birthed many new stars. These young stars are visible in the faint bridge connecting the two galaxies, located at the bottom of the image. Such a bridge provides an avenue for the two galaxies to continue sharing the gas and dust that becomes new stars. Scientists believe Arp 271 can serve as a blueprint for future interactions between our Milky Way Galaxy and our neighbor the Andromeda Galaxy, expected to happen in about 4 billion years.
LEARN MORE:
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
Share
Details
Related Terms
First published at NASA.gov








