Altitude Chamber Gets Upgrade for Artemis II, Spacecraft Testing Begins
Before the Orion spacecraft is stacked atop NASA’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) rocket ahead of the Artemis II mission, engineers will put it through a series of rigorous tests to ensure it is ready for lunar flight. In preparation for testing, teams at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida have made significant upgrades to the altitude chamber where testing will occur.
Several of the tests take place inside one of two altitude chambers in the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at Kennedy. These tests, which began on April 10, include checking out electromagnetic interference and electromagnetic compatibility, which demonstrate the capability of the spacecraft when subjected to internally and externally generated electromagnetic energy and verify that all systems perform as they would during the mission.
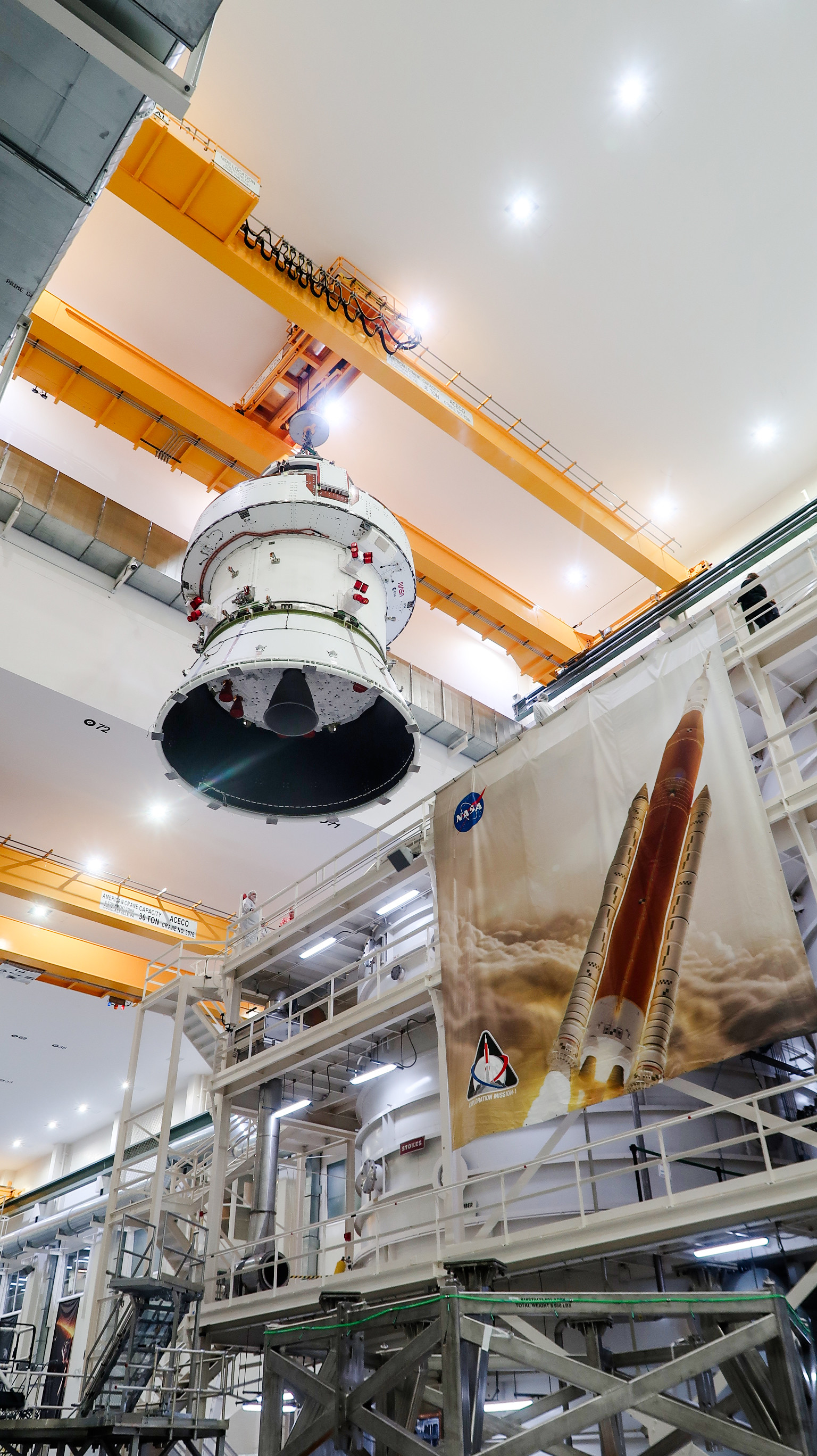
To prepare for the tests, the west altitude chamber was upgraded to test the spacecraft in a vacuum environment that simulates an altitude of up to 250,000 feet. These upgrades re-activated altitude chamber testing capabilities for the Orion spacecraft at Kennedy. Previous vacuum testing on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I took place at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Ohio. Teams also installed a 30-ton crane in the O&C to lift and lower the Orion crew and service module stack into the chamber, lift and lower the chamber’s lid, and move the spacecraft across the high bay.
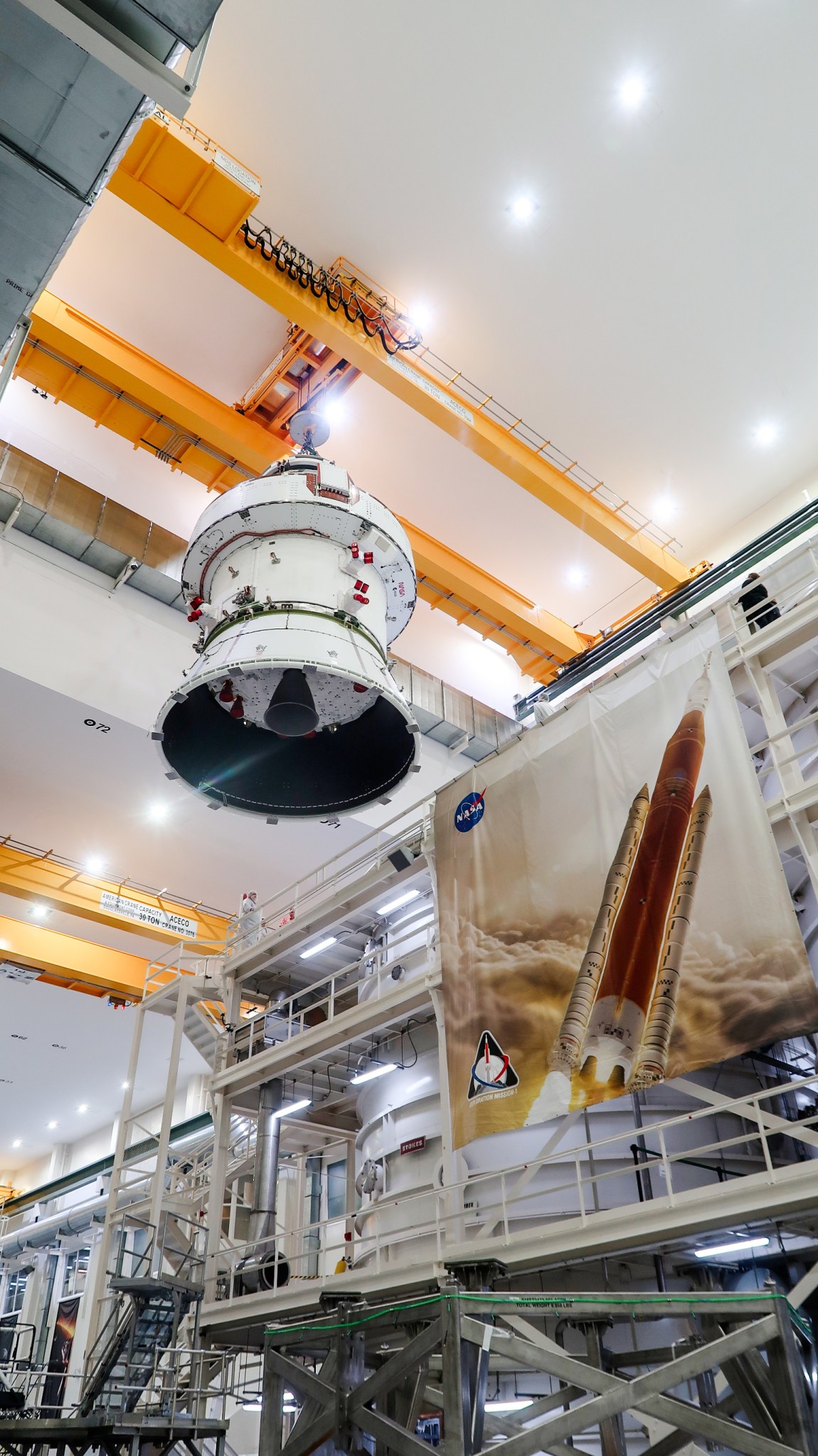

On Thursday, April 4, teams loaded the Artemis II spacecraft into the altitude chamber. This event marks the first time, since the Apollo testing, that a spacecraft designed for human exploration of space has entered the chamber for testing. After testing is complete, the spacecraft will return to the Final Assembly and Systems Testing, or FAST, cell in the O&C for further work. Later this summer, teams will lift Orion back into the altitude chamber to conduct a test that simulates as close as possible the conditions in the vacuum of deep space.
Originally used to test environmental and life support systems on the lunar and command modules during the Apollo Program, the interior of each altitude chamber measures 33 feet in diameter and 44 feet high and was designed to simulate the vacuum equivalent of up to 200,000 feet in a deep space environment. Both chambers were rated for astronaut crews to operate flight systems during tests.
After Apollo, the chambers were used for leak tests on pressurized modules delivered by the Shuttle program for the International Space Station.

Additional upgrades to the west chamber include a new oxygen deficiency monitoring system that provides real-time monitoring of the oxygen levels and a new airflow system. New LED lights replaced the previous lighting system, and equipment from the Apollo days was removed. A pressure control system was added to the chamber that provides precise control of pressure levels. Two new pumps remove the air from the chamber to create a vacuum. New guardrails and service platforms replaced the older platforms inside the chamber.
A new control room overlooks the upgraded chamber. It contains several workstations and communication equipment. The chamber control and monitoring system was upgraded to handle operation of all the remotely controlled hardware and subsystems that make up the vacuum testing capability.
“It was an amazing opportunity to lead a diverse and exceptional team to re-activate a capability for testing the NASA’s next generation spacecraft that will carry humans back to the Moon,” said Marie Reed, West Altitude Chamber Reactivation Project Manager. “The team of more than 70 aerospace professionals, included individuals from NASA, Lockheed Martin, Artic Slope Research Corps, Jacobs Engineering, and every discipline area imaginable. This project required long hours of dedication and exceptional coordination to enable the successful turn-around and activation in time for this Artemis II spacecraft testing.”

NASA’s Artemis II mission will carry four astronauts aboard the agency’s Orion spacecraft on an approximately 10-day test flight around the Moon and back to Earth, the first crewed flight under Artemis that will test Orion’s life support systems ahead of future missions. Under the Artemis campaign, NASA will return humanity to the lunar surface, this time sending humans to explore the lunar South Pole region.
For time lapse footage of the Artemis II lift into the vacuum chamber visit: Artemis II Orion Vac Chamber Lift and Load Operations
First published at NASA.gov





